The Benefits of a Mediterranean Diet: Why You Should Consider Making the Switch
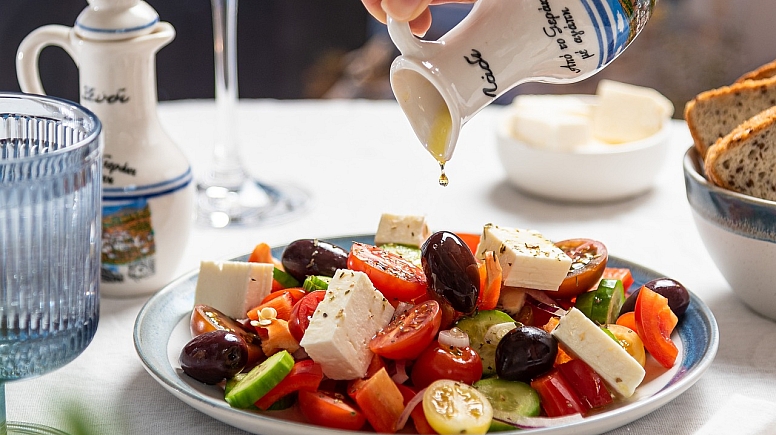
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that is inspired by the traditional dietary patterns of people who live in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Turkiye, Greece, Italy, and Spain.
This diet emphasizes the consumption of whole foods, whole grains, nuts, and legumes, as these foods are high in fibre, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are essential for maintaining good health, along with moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy, and a limited intake of red meat and sweets.
Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
Research has shown that the Mediterranean diet can offer a range of health benefits. Here are just a few:
Reduced Risk of Heart Disease: One of the key health benefits of the Mediterranean diet is its ability to reduce the risk of heart disease. Studies have shown that people who follow the Mediterranean diet have lower levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides, which can lead to a reduced risk of heart disease. The diet is also associated with lower rates of stroke, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Improved Cognitive Function: Another benefit of the Mediterranean diet is its potential to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease. Studies have suggested that the diet's emphasis on healthy fats, such as olive oil, and anti-inflammatory foods, such as berries and leafy greens, can help protect the brain from damage and improve cognitive function.
Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: The Mediterranean diet is also beneficial for people with diabetes. The diet's emphasis on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. The diet's anti-inflammatory properties may also be helpful for people with diabetes, as inflammation is a key factor in the development of the disease.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: The Mediterranean diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts, which can help reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Weight Management: Weight management is another potential benefit of the Mediterranean diet. While the diet is not a weight loss diet, it has been associated with weight loss and weight management due to its emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods and limited intake of processed foods and sweets. This can help reduce calorie intake and promote healthy weight loss.
How to Incorporate the Mediterranean Diet into Your Lifestyle

If you're interested in adopting a Mediterranean-style eating pattern, here are some tips:
Eat plenty of vegetables: Vegetables should make up a large portion of your meals. Aim for at least 2-3 servings of vegetables per meal.
Choose healthy fats: Use olive oil as your primary source of fat, and incorporate other healthy fats like nuts, seeds, and avocado.
Eat seafood regularly: Fish and seafood are a key part of the Mediterranean diet, and should be consumed at least twice a week.
Limit red meat: Red meat should be limited to a few times a month.
Enjoy whole grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered to be a healthy way of eating, there are a few potential drawbacks and considerations to keep in mind:
Cost: Some of the key components of the Mediterranean diet, such as fresh seafood and high-quality olive oil, can be expensive depending on where you are buying them from.
Allergies and Intolerances

If you have allergies or intolerances to certain foods, such as nuts or seafood, you may need to modify the Mediterranean diet to suit your needs. Here are some tips:
Substitute nuts with seeds: If you are allergic to nuts, you can substitute them with seeds such as pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, or sesame seeds. These seeds are also nutrient-dense and rich in healthy fats, making them a good replacement for nuts.
Incorporate other sources of protein: Seafood is a key component of the Mediterranean diet, but if you are allergic to seafood, you can incorporate other sources of protein, such as beans, lentils, tofu, or chicken. These foods are also nutrient-dense and can provide you with the protein your body needs.
Use alternative oils: If you are allergic to nuts, you may need to avoid using nut-based oils, such as walnut or almond oil. Instead, you can use other healthy oils, such as olive oil, coconut oil, or avocado oil, which are not derived from nuts.
Be cautious when dining out: When dining out, make sure to inform the waiter or chef about your allergies, so they can modify the dish or suggest an alternative. It's important to be cautious when dining out and to always double-check the ingredients used in the dish.
Focus on other Mediterranean foods: While seafood and nuts are common in the Mediterranean diet, there are plenty of other nutritious foods that you can incorporate into your meals, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats like olive oil. You can focus on these foods to ensure that you are still getting the nutrients and health benefits of the Mediterranean diet.
It's important to note that if you have a severe allergy, it's best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs while avoiding potential allergens.
Cultural Differences

Depending on your cultural background and food preferences, it may take some time to adjust to the flavours and ingredients used in the Mediterranean diet.
Mediterranean food is not generally considered to be spicy. Many Mediterranean dishes are known for their simple, yet flavourful ingredients and herbs, such as olive oil, garlic, lemon, and fresh herbs like basil, parsley, and oregano.
While some Mediterranean dishes, particularly those from North African countries like Morocco and Tunisia, may incorporate spicy ingredients like harissa or cumin, the cuisine as a whole is not known for being particularly spicy. However, this can vary depending on the specific dish and the region it comes from.

It's important to note that while the Mediterranean diet is generally considered to be a healthy way of eating, there are a few potential drawbacks and considerations to keep in mind. For example, some of the key components of the Mediterranean diet, such as fresh seafood and high-quality olive oil, can be expensive. Additionally, if you have allergies or intolerances to certain foods, such as nuts or seafood, you may need to modify the diet to suit your needs.
Overall, the Mediterranean diet is a healthy and sustainable way of eating that can offer a range of health benefits. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and limiting processed foods and sweets, you can improve your health and reduce your risk of chronic disease.
Whether you're looking to lose weight, improve your heart health, or simply enjoy delicious and nutritious meals, the Mediterranean diet is worth considering.